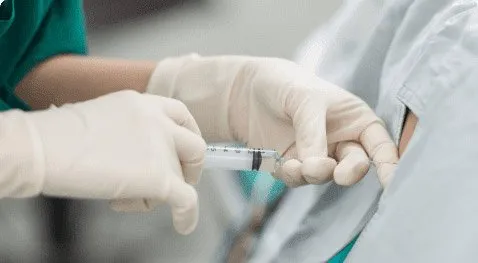
The American Society of Pain and Neuroscience (ASPN) issued a new set of recommendations to guide clinicians in the safe and appropriate use of steroid injections for pain management in patients who are receiving the COVID-19 vaccine (J Pain Res 2021;14:623-629).
“The central question that we wanted to deduce and answer is whether a local steroid injection might potentially reduce the efficacy of the COVID-19 vaccine, which relies upon a robust and potent immune response that primes the body to fight the virus,” lead author Krishnan Chakravarthy, MD, PhD, an assistant clinical professor of anesthesiology at the University of California, San Diego, told Pain Medicine News.

Lumbar radiculopathy is one of the most common patient complaints. In fact, three to five percent of the population complain of lumbar radicular pain, and even more people struggle with the pain in silence.
From spine surgeons to pain management physicians, these patients often become frustrated as they have no understanding of what’s happening. It is imperative for these patients to understand what lumbar radicular pain is and what the common treatments are.
What Is Lumbar Radicular Pain?
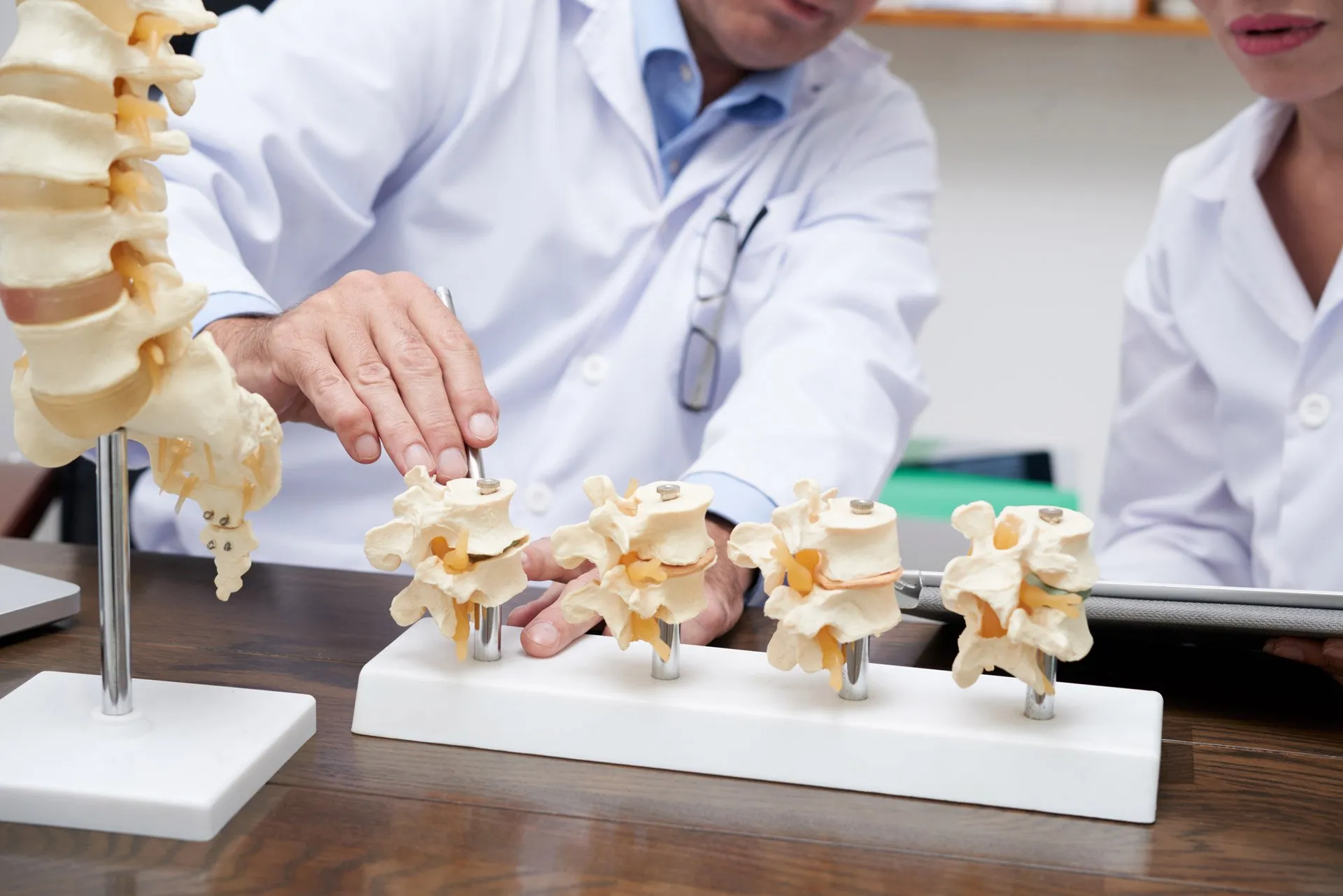
Lumbar radiculopathy is a kind of disease in the lower spine. More specifically, this condition involves the nerve roots in the lumbar spine. Those with it may experience pain, numbness, and/or weakness in the buttock and/or one of the legs. Often, people use the term sciatica to refer to lumbar radicular pain. If the spinal nerve root becomes compressed, this can lead to lumbar radicular pain. This is the most common cause of the condition.
Because of the compression of the nerve, the pain can refer to other areas. Most often, this pain refers to one of the legs. Delaying care by ignoring the pain can lead to further damage of these nerves and/or nerve roots. Because lumbar pain is so common, your physician is likely to have seen many cases before. They should be able to help you find the source of the problem and get your pain under control.
What Causes Lumbar Radiculopathy?
When the spinal nerve roots become irritated or compressed, lumbar radiculopathy may form. Irritation and/or compression can develop because of mechanical manipulation or result from another condition such as:
- Lumbar disc herniation
- Spinal stenosis
- Osteophyte formation
- Spondylolisthesis
- Foraminal stenosis
In fact, many degenerative disorders could cause lumbar radiculopathy.
How Can I Get A Diagnosis For Lumbar Pain?
You can get a diagnosis from a spinal doctor, a chiropractor, an orthopedic physician, a primary care doctor, or similar specialist. Whoever you see will look over your medical history and give you a physical examination.
While they’re examining you, the physician will look at your spinal range of motion, movement limitations, balance issues, and sensory issues. These sensory issues may include loss of extremity reflexes, muscle weakness, or abnormal reflexes.
The physician may also decide to get an x-ray or MRI to view your spinal structure. However, if you have a contraindication like a pacemaker or a spinal cord stimulator, you may get a CT myelogram instead of an MRI.
What Are The Symptoms Of Lumbar Radicular Pain?
Not every patient’s lumbar pain is the same. But, here are some of the most common complaints associated with lumbar radiculopathy:
- Pain
- Tingling
- Numbness
- Weakness
- Loss of reflexes
These kinds of symptoms typically happen in the lower back, buttocks, leg, and foot. The pain can radiate to either leg, but it usually only affects one leg.
If you’re having any of these symptoms, see a doctor as soon as possible. If you continue to use your spine as normal, you could cause more damage. It’s important to get to the root of the problem so that you know you aren’t hurting yourself.
What Are The Treatments For Lumbar Radiculopathy?
If you’re suffering from lumbar radicular pain, there are a few kinds of treatments that your doctor may mention. These fall into two categories: surgical and non-surgical.
Physicians start out by testing non-surgical techniques unless your results show a strong need for surgery.
Non-Surgical Treatments for Lumbar Radicular Pain
There are a couple of non-surgical options for correcting lumbar pain:
- Physical therapy
- Pain management
- Injections
Your physician may decide that you need one, two, or all three. You could even do all of them at once or try two or three at a time. There is no right or wrong order because it depends on your particular case.
Physical therapy can go through a prescription process or involve you doing muscle exercises at home. Either way, the movements that the patient does are meant to stabilize the spine. This can help your body make more room for the spinal nerve roots so that they can decompress. Pain management involves administering medications to someone with lumbar radiculopathy. These can range from non-steroidal anti- inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) to steroidal medications.
The kinds of medications that your physician recommends will depend on your level of pain and your use of medications in the past. These medications should help reduce swelling and pain.
The injections that you could get include an epidural steroid injection and/or a nerve root injection. These can help reduce swelling and pain that radiates into your hips. It should also be able to help with the pain that radiates down into the leg, no matter which leg the pain is affecting.
Surgical Treatments for Lumbar Radicular Pain
The kinds of surgical treatments that you can have depend on what is causing your lumbar pain. Most of these kinds of surgeries work to decompress the nerve or stabilize the spine.
There are various types of surgical treatments to help alleviate your lumbar radicular pain, including spinal fusion, laminotomy, laminectomy, and microdiscectomy.
These surgeries work to fix deformities in the spine and its nerves. By having the appropriate surgery done, you could find relief from your lumbar radicular pain.
Pain Management For Lumbar Radicular Pain
Pain management for lumbar radicular pain is important. Whether your physician opts for non-surgical or surgical techniques, you need to get the pain under control before additional problems arise.
If you’re looking for treatment options, our team at Interventional Pain and Spine is here for you. We will customize a treatment plan to get you through your lumbar pain.
Contact us today to make an appointment.